Formula for common geometric shapes for GK
Formulas of Common Geometric Shapes
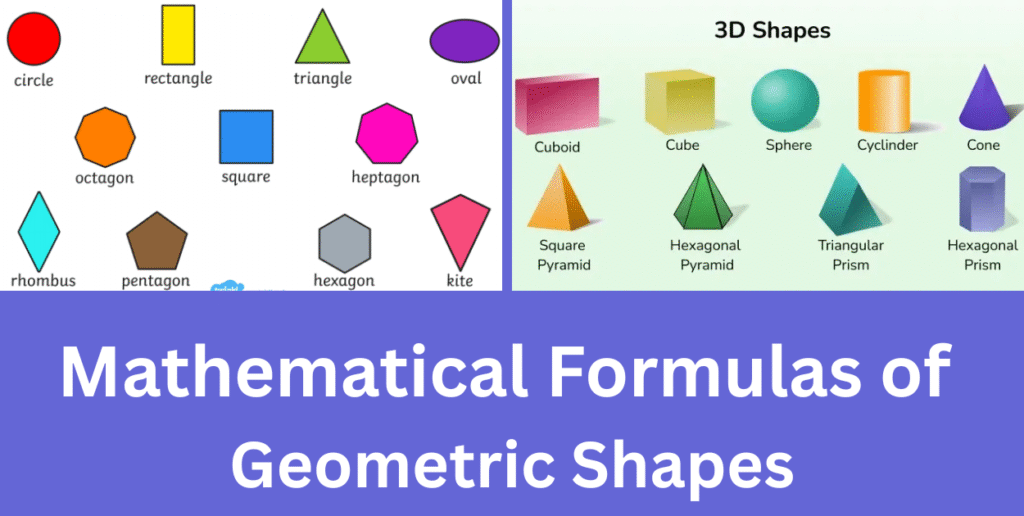
Formulas of Common Geometric Shapes
(2D and 3D) (With Diagrams)
(Easy GK Notes for School & Competitive Exam Students)
Understanding basic geometry shapes is important for GK, Maths, and entrance exams. Below are simple formulas with diagram examples to make learning easy.
🟩 2D Shapes (Flat Figures)
| Shape | Diagram | Formula |
|---|---|---|
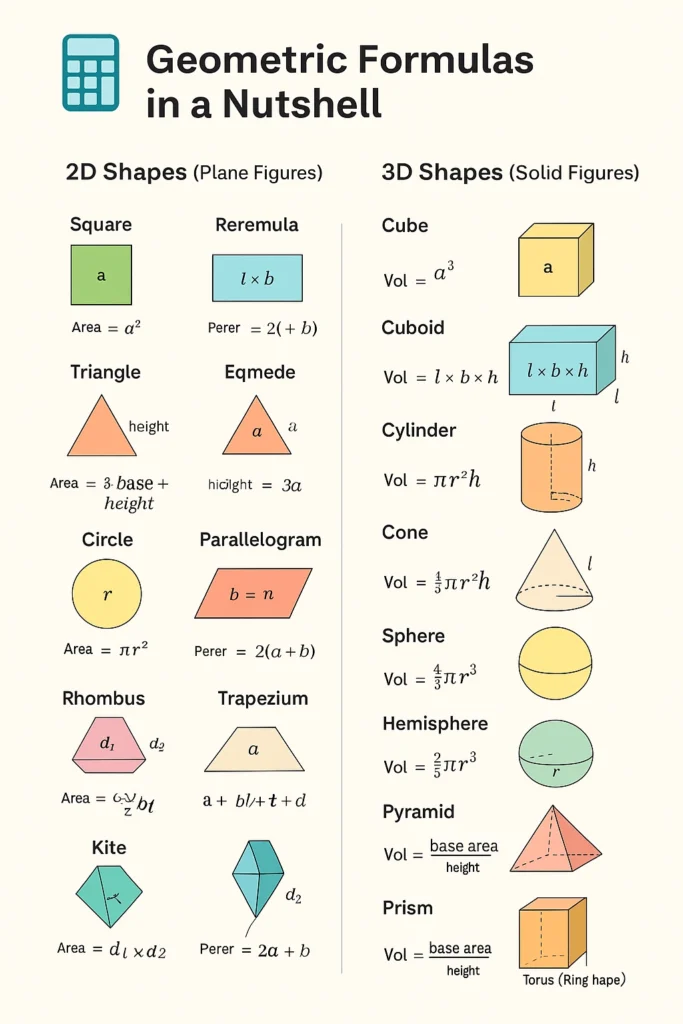
| Square | ⬜ | Area = a² Perimeter = 4a |
| Rectangle | ▭ | Area = l × b Perimeter = 2(l + b) |
| Triangle | 🔺 | Area = ½ × base × height Perimeter = a + b + c |
| Circle | ⚪ | Area = πr² Circumference = 2πr |
| Parallelogram | ▰ | Area = base × height Perimeter = 2(a + b) |
| Trapezium (Trapezoid) | ⏢ | Area = ½ × (sum of parallel sides) × height |
Formula for Common Geometric Shapes
🟦 3D Shapes (Solid Figures)
| Shape | Diagram | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Cube | ◼️ | Volume = a³ Surface Area = 6a² |
| Cuboid | 📦 | Volume = l × b × h Surface Area = 2(lb + bh + hl) |
| Cylinder | 🧯 | Volume = πr²h Surface Area = 2πr(h + r) |
| Cone | 🍦 | Volume = ⅓πr²h Surface Area = πr(l + r) |
| Sphere | ⚽ | Volume = ⁴⁄₃πr³ Surface Area = 4πr² |
| Hemisphere | 🥣 | Volume = ⅔πr³ Surface Area = 3πr² |
Quick Tips for Students:
-
Use π = 3.14 or 22/7.
-
Area is always in square units (cm², m²).
-
Volume is in cubic units (cm³, m³).
-
Draw and label shapes while learning to avoid confusion.
Formula for Common Geometric Shapes
Algebra Formulas
| Formula Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| (a + b)² | a² + 2ab + b² |
| (a − b)² | a² − 2ab + b² |
| a² − b² | (a + b)(a − b) |
| (a + b + c)² | a² + b² + c² + 2(ab + bc + ca) |
| (a + b)³ | a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³ |
| a³ + b³ | (a + b)(a² − ab + b²) |
| a³ − b³ | (a − b)(a² + ab + b²) |
Tip for Exams
-
Memorize π = 22/7 or 3.14
-
Know Pythagoras Theorem: a² + b² = c²
-
Learn unit conversions:
-
1 km = 1000 m
-
1 m = 100 cm
-
1 litre = 1000 ml
-
Geometry Formulas (3D Shapes / Mensuration)
| Solid Shape | Diagram | Volume | Surface Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cube | ⬛ | a³ | 6a² |
| Cuboid | 📦 | l × b × h | 2(lb + bh + hl) |
| Cylinder | 🧯 | πr²h | 2πr(h + r) |
| Cone | 🔺 (3D) | (1/3)πr²h | πr(l + r) where l = √(r² + h²) |
| Sphere | ⚽ | (4/3)πr³ | 4πr² |
| Hemisphere | ⚪⬇ | (2/3)πr³ | 3πr² (TSA), 2πr² (CSA) |
📘 Trigonometry (Basic)
| Ratio | Formula |
|---|---|
| sinθ | Perpendicular / Hypotenuse |
| cosθ | Base / Hypotenuse |
| tanθ | Perpendicular / Base |
| cotθ | 1 / tanθ |
| secθ | 1 / cosθ |
| cosecθ | 1 / sinθ |
Important Identities:
-
sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
-
1 + tan²θ = sec²θ
-
1 + cot²θ = cosec²θ
Pythagoras Theorem (पाइथागोरस प्रमेय) – आसान भाषा में समझिए
📘 परिचय (Introduction)
पाइथागोरस प्रमेय (Pythagoras Theorem) गणित का एक बहुत ही महत्वपूर्ण सूत्र है, खासकर त्रिभुज (Triangle) के अध्याय में।
यह प्रमेय केवल समकोण त्रिभुज (Right-Angled Triangle) पर लागू होता है।
यह प्रमेय प्राचीन यूनानी गणितज्ञ पाइथागोरस (Pythagoras) द्वारा खोजा गया था।
पाइथागोरस प्रमेय क्या कहता है? (What the Theorem Says)
हिंदी में:
किसी समकोण त्रिभुज में, कर्ण (Hypotenuse) की लंबाई का वर्ग, अन्य दो भुजाओं (Base और Perpendicular) के वर्गों के योग के बराबर होता है।
English Version:
In a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (base and perpendicular).
Formula (सूत्र)
Hypotenuse2=Square of Base +Square of Perpendicular






